In recent years, Karnataka Bank has been actively expanding its national footprint, increasing its branch network to 931 as of Q2FY25. The bank aims to transition from a regional player to a prominent national banking institution.
- About the company
- Journey Since Inception
- Board Members
- Shareholding Pattern
- Business Segments
- Revenue Segments
- Cost Structure
- Financial Parameters
- Management Key Highlights
- Strengths & Weaknesses
(A) About
Karnataka Bank, based in Mangalore, was established in 1924. It consists of a network of 921 branches spread across 22 states and 2 Union Territories. The bank caters to the needs of the people by providing them with banking/financial products and services.
The bank’s total business turnover as of Q2FY25 exceeded 1,75,284 crores, which included deposits of 99,968 crores and advances of 75,316 crores.
Recently, the bank has concentrated on establishing itself as a digital-first bank, as seen by several initiatives and investments in IT infrastructure. The bank also strives to present itself as a ‘Pan-India’ bank, as evidenced by its ‘Bharat Ka Karnataka Bank’ campaign.
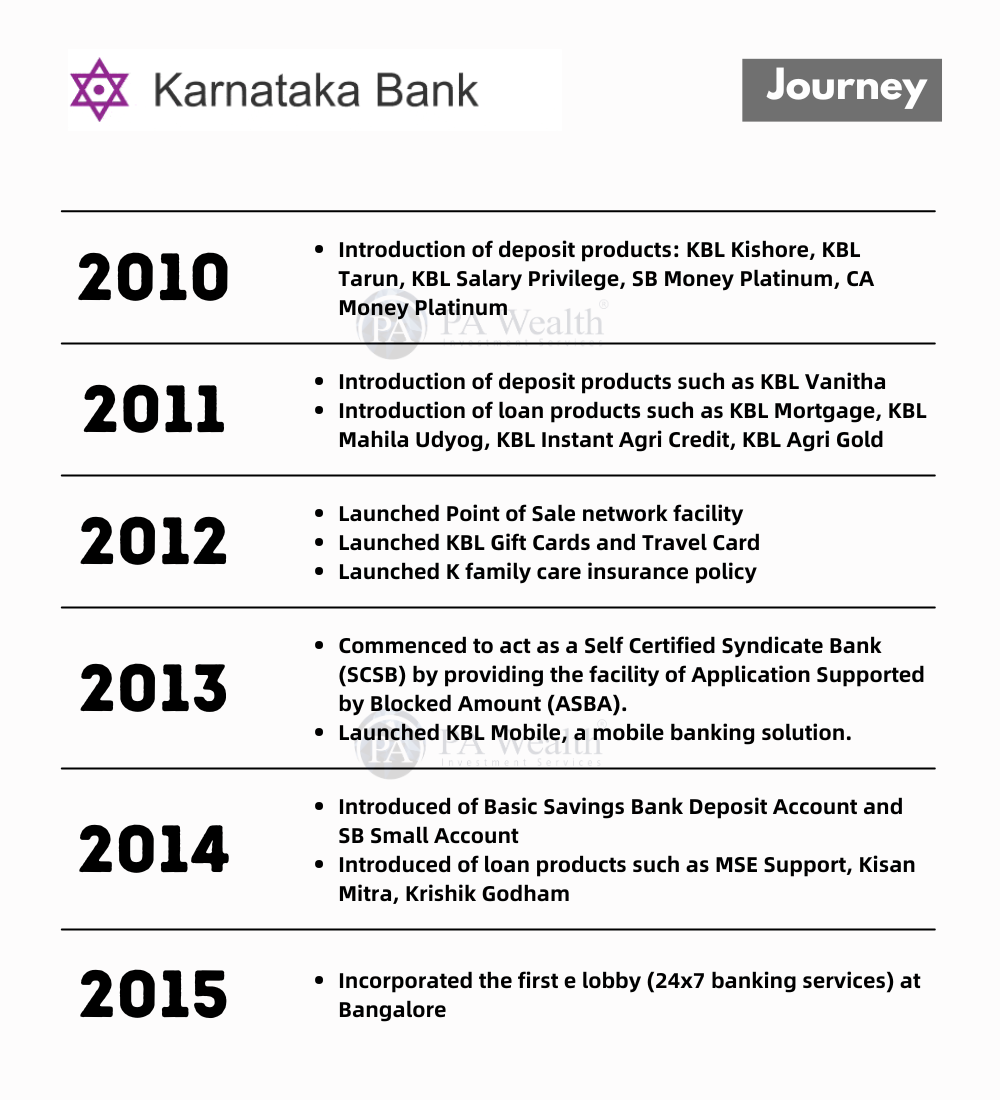
(B) Journey of Karnataka Bank
(C) Board of Directors of Karnataka Bank
(D) Indian Banking Industry
Profitability
Banks are likely to continue to have excellent profitability but may experience challenges on net interest margins (NIM) over the next two years, with a possible reduction of 10 to 20 basis points from the present top of 3.6%. This compression is substantial given that NIMs account for nearly 75% of banks’ total operating revenue. The fall in Net Interest Income is primarily linked to growing lending costs due to greater competition for deposits and the normalization of liquidity circumstances despite strong loan growth.
Operational Costs
To counterbalance the narrowing margins, banks are concentrating on lowering operational and credit costs through better cost management methods and efficiency benefits driven by digitization. Additionally, banks are reallocating investments from government securities to loan growth, which increases risk density due to larger risk appetites, to reduce margin pressures.
Asset Coverage
The share of loans in banks’ total assets has increased from 56% in FY22 to 63% in FY23. Meanwhile, the average liquidity coverage ratio remains healthy at 127%, substantially over the statutory minimum of 100%, giving banks significant headroom for managing liquidity.
Advances and Deposits
The loan-to-deposit ratio has risen from 75% in FY23 to 79% in FY24, with a minor increase to 81% recently. However, the share of low-cost deposits has declined to 39%, driven by heightened competition and rising term deposit costs. In terms of funding and liquidity management, client deposits remain the dominant source, accounting for 90% of non-equity funding for banks.
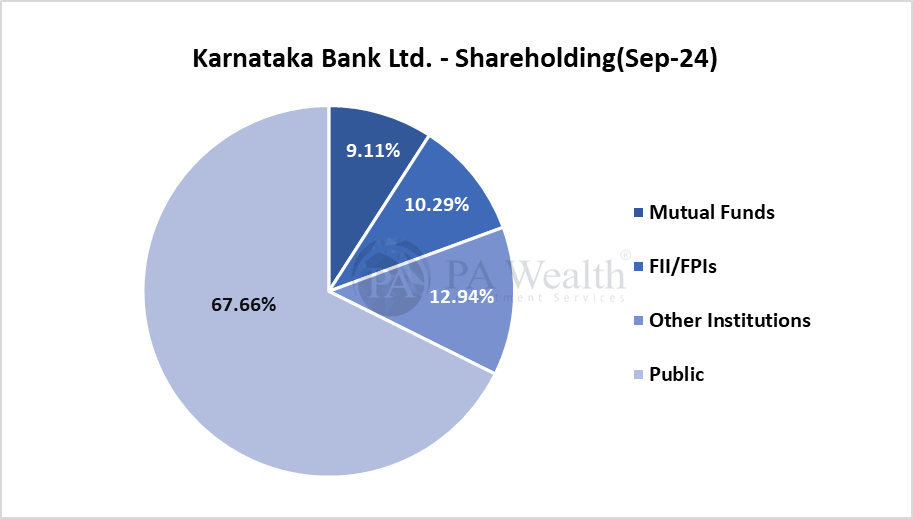
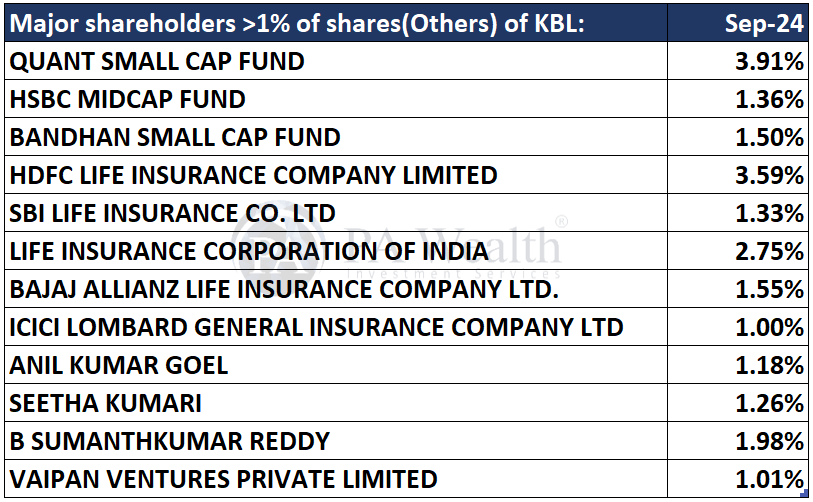
(E) Shareholding Pattern of Karnataka Bank
(F) Business Segments
Treasury Operations
The Treasury segment is critical to managing statutory reserves by ensuring compliance with the Reserve Bank of India’s regulatory standards, such as the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) and Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR). To improve the bank’s financial performance, the department focuses on effective liquidity management, as well as investment and trading.
It manages short-term surplus liquidity by investing in sovereign debt instruments, other fixed-income assets, commercial papers, mutual funds, and certificates of deposit. Furthermore, the Treasury division is heavily involved in foreign currency operations and services, providing forward contracts and foreign exchange products that meet customer demands.
Retail Banking
This segment offers a diverse range of financial offerings through various channels, including loans for homes, autos, education, personal needs, against term deposits and stocks, gold, and small companies. The bank prioritizes sectors like agriculture, MSMEs, housing, and education, and provides customized solutions. The retail division offers loans up to ₹7.5 crores for various industries, services, agricultural, forex, and business operations. It is supported by four specialized wings: agricultural, Forex, SMEs, and Others.
This segment also offers liability products for Current and Savings Accounts and offers personalized solutions for Salaried Individuals, Senior Citizens, Corporations etc. This also includes other products such as term deposits and recurring deposits.
The bank also facilitates government banking which includes the collection of Direct Taxes, Custom Duty and GST, offering multiple payment methods Flexi Fixed Deposit facilities for government agencies such as the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) and Direct Tax (Income Tax/Advance Tax) on behalf of Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT).
Corporate/Wholesale Banking
This segment serves large corporations, public entities, and private firms, providing a complete range of financial solutions. It offers fund-based and non-fund goods, such as term loans, working capital facilities, and foreign exchange services. It also specializes in structured finance and trade financing solutions, such as letters of credit, guarantees, and bill discounting.
Other Banking Operations
This segment includes a variety of third-party products and services that complement its core banking offerings:
This includes co-lending partnerships with NBFCs including Paisalo Digital Ltd., Satin Creditcare, Clix Capital, Yubi, and Northern Arc to expand lending possibilities. The bank is also heavily involved in bancassurance, collaborating with five companies—LIC, PNB MetLife, Bharti AXA Life, and HDFC Life—to market life, general, and health insurance products as a registered corporate agent under IRDA regulations.
Karnataka Bank distributes mutual fund products has been empanelled with 8 AMCs via its branch network and sells mutual funds online by patterning with FISDOM, which is incorporated into its mobile app.
As a CDSL participant, the bank offers depository services and online trading through cooperation with Way2Wealth, IIFL, and FISDOM.
Locker facilities and a full card services portfolio are available, including a debit card base created in partnership with the Visa and RuPay networks.
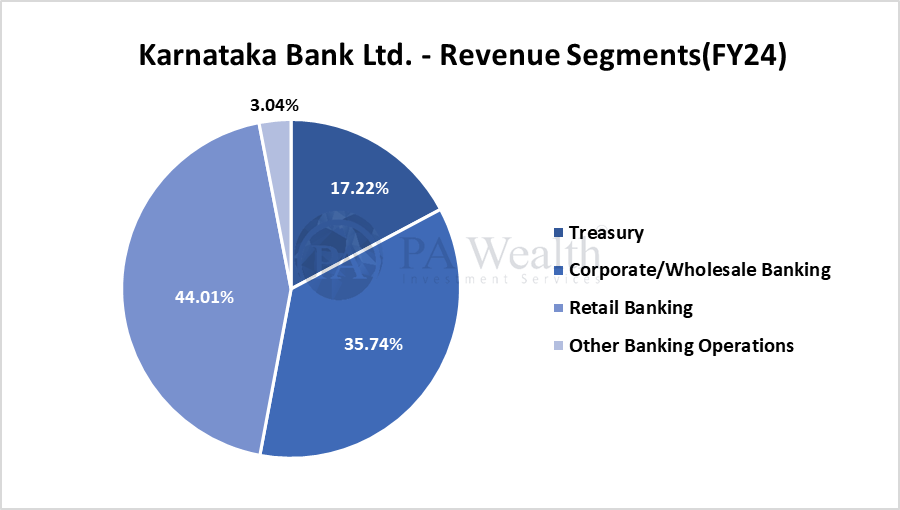
(G) Revenue Segments
(H) Operational Network of Karnataka Bank
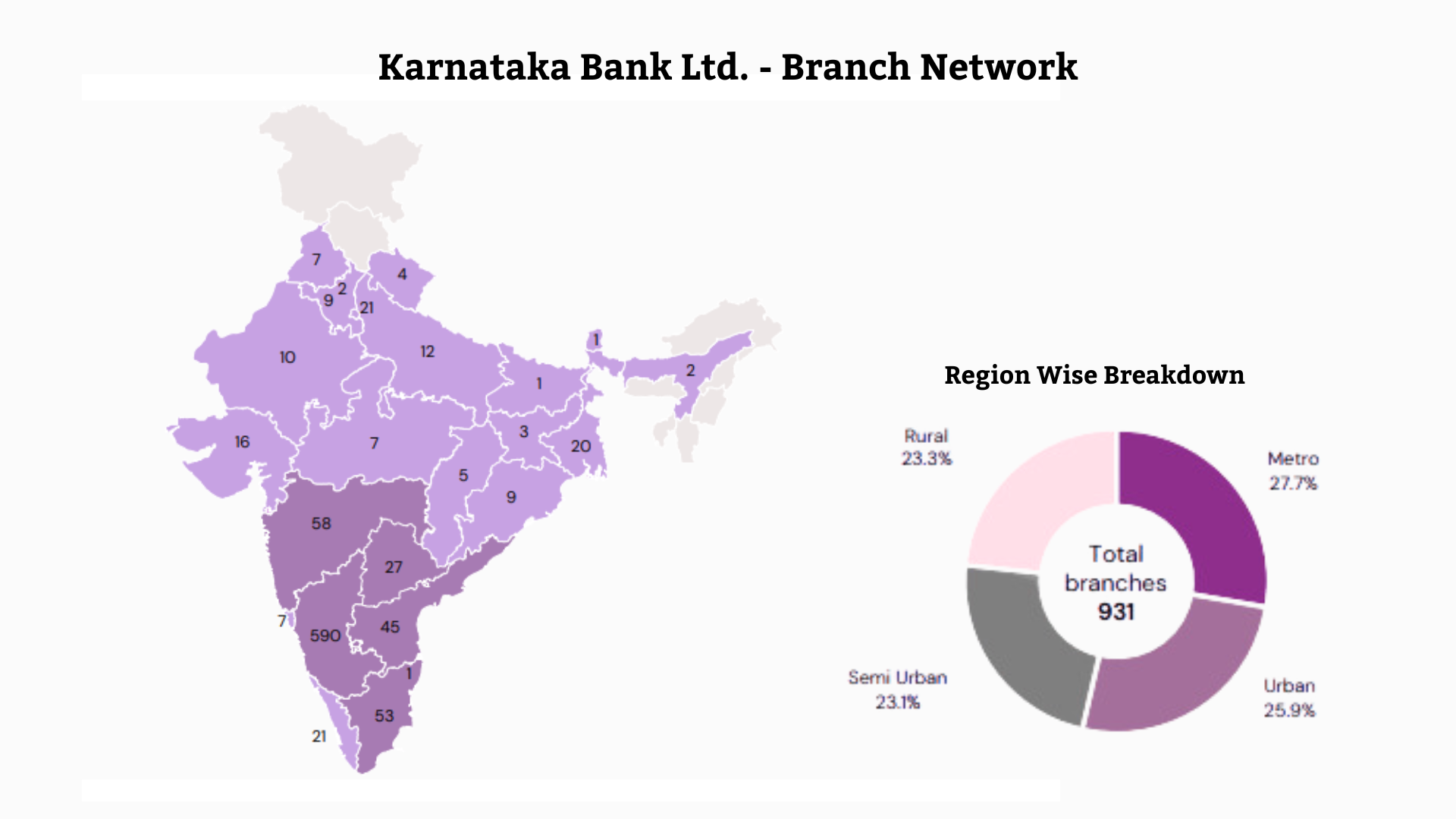
The bank has around 2417 Services which comprise 931 Branches, 1 Extension, 856 ATMs, 639 Recyclers, 1 Data Center, 2 Service branches, 5 Currency Chests, 2 Central Processing Centres, 1 Digital Centre, 9 Asset Recovery Branches, 3 Central Loan Processing Hub, 1 Central Loan Sanctioning Centre.
The Bank recently introduced a cluster-based management approach, organising its branches into 51 clusters to improve operational efficiency. Furthermore, the bank has made structural changes to its management hierarchy, with sales and coverage teams now operating independently of the branch organization. Previously, the branch head was solely responsible for managing the branch and sales activities. The new structure enables more focused management and increased effectiveness at all levels.
(I) Financials of Karnataka Bank
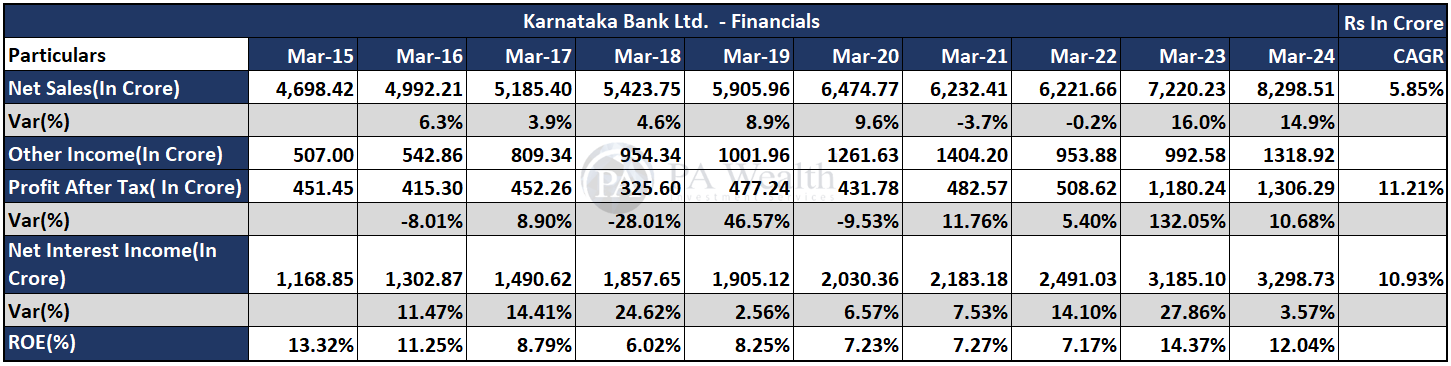
The company’s revenue has grown at a CAGR of 5.85% over the past 10 years from Rs 4698.42 Cr. in FY15 to Rs 8298.51 Cr. in FY24. Subsequently, The company’s PAT has grown from Rs 451.45 Cr. in FY15 to Rs 1306.29 Cr. in FY24 at a CAGR of 11.21%. Furthermore, the company’s ROE slightly decreased from 13.32% in FY15 to 12.04% in FY24.
Ratios
(J) Management Discussion
Outlook
The bank achieved its highest-ever business turnover and Net profit in FY24, standing at ₹1,71,059.49 Crores and 1306.28 Cr. Non-interest income surged to 1318.92 Cr. a growth of 32.88% YoY
Concall Highlights
- ROA of the bank is 1.13% for Q2, targeting 1.2% to 1.25% over the next few quarters.
- Net accretion of the retail book was about INR 1,300 crores for Q2FY25 with a focus on quality over profitability.
- Interest income remained stable with a slight fluctuation of around INR 30 crores. NIMs declined by 30 bps due to deploying INR 4,000 crores of excess liquidity.
- Maintaining a 50% mix from retail loans and the remaining 50% from direct corporate loans. Asset acquisition strategy focusing on retail and direct corporate segments for higher yields.
- Slippages guidance at 0.5%, including actual additions to NPA, reductions, and recoveries. Slippages guidance based on gross slippages minus recoveries and upgrades.
- Maintaining ROE guidance range of 1.2% to 1.4% despite temporary blips in the quarter
- Transition adjustments for securities available for sale are now contributed to the AFS reserve, rather than profit, under the new policy by RBI.
- The bank achieved gross advances of 75,316 Cr., a 12.5% increase YoY. Gross Advances grew to 99,968 Cr as of Q2FY25, an increase of 11.7% YoY, The Majority of this came from Retail Advances. The company focuses on Mid-corporate and RAM(Retail, Agriculture and MSME) Segments for future growth.
- Bank’s deposits reached a new high of ₹99,968 Cr., increasing 11.7% YoY and decreasing (0.2%) QoQ. However, the CASA ratio was 30.82% as of Q2FY25, with management recognizing the need for improvement. They attributed the lower CASA ratio to a broader industry trend but plan to launch various new product offerings to drive future CASA growth.
- In Q2FY25, The Bank reported a Net Interest Income of ₹834 Cr., down from ₹903 Cr. in Q1FY25.
Interest Margins
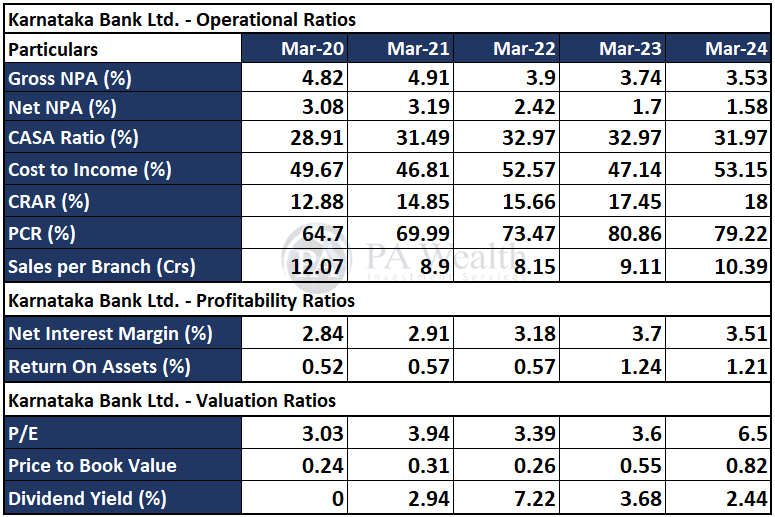
- Net Interest Margin decreased to 3.23% from 3.54% in Q2FY25. Cost of funds reached 5.58% in Q2FY25.
- Management ascribed the decline in NIM to stretched market liquidity and difficulties in sourcing deposits. This has also hurt the broader banking sector. It has also provided guidance of 3.5% to 3.7% for FY25.
- Most of the bank branches contributed to deposit growth as the network increased to 931. Most branches reported increased retail term deposits, CASA growth, and liability products. To increase CASA growth, the bank will launch new bundled CASA services in the next two quarters.
Ratios
- The cost-to-deposit ratio rose to 75.34% in Q2FY25, up from 74.76% in Q1FY24. Despite this, the bank continues to have excess liquidity. Additionally, Treasury’s excess liquidity will be lent into the market which is projected to increase yields by 70 to 90 bps. This may improve earnings in the next quarters.
- Q2FY25 Provision Coverage Ratio (PCR) was 80.14%, up 217 basis points from Q1FY25’s 77.97%. Management is optimistic that the bank’s asset quality will be maintained and improved.
NPAs and Restructured Assets
- As of Q2FY25, the Bank’s Gross NPA (GNPA) ratio stood at 3.21%, a marginal decrease from 3.54% in Q1FY25. However, on a larger basis, contracted by 14 bps from 3.47% in Q2FY24.
- Net NPA for Q2FY25 is 1.46% decreased from 1.66% in Q1FY25.
- Total GNPA for Q2FY25 amounted to ₹2415 crore.
- Provisional technical write-offs stood at ₹3100 crore as of Sep 2024, with the bank expecting these amounts to remain uncollectible and possibly requiring write-offs in the future.
- Gross slippages were 0.33% in Q2 FY25, down from 0.59% in Q1 FY25. Recoveries for Q2FY25 amounted to ₹148.01 crore, ₹133.12 crore in Q1 FY25 and ₹117.82 crore in Q1FY24.
Restructured Advances
- The combined GNPA and restructured advances ratio for Q2 FY25 was 4.9%, compared to 5.4% in Q1 FY25 and 6.8% in Q2 FY24.
- In Q2 FY25, total additions/slippages amounted to ₹242.67 crore. Most of the retail restructured portfolio has been addressed, except for 10 to 20 bigger accounts.
- Granular components like home loans in the restructured book have been reformed and are migrating into the regular portfolio.
- 91% of the restructured loan book is collateral-backed and forecasts a decline in this portfolio over the next 2-3 quarters. A special team, supervised by the credit monitoring department, has been deployed to handle these recoveries.
- Around 50% of GNPAs derive from the historical loan book, which does not include the restructured component. The bank has provisioned for at least 14-15% of this old book and is currently striving to clean it up.
- The majority of GNPAs come from the mid-market and agricultural sectors, which are part of the older loan portfolio. The restructured book, now cut to ₹1,160 crore, is anticipated to drop further in the coming quarters.
- Karnataka Bank took a conservative strategy during the epidemic, adding ₹4,500 crore in NPAs and restructured assets. However other banks did not go the same route. However, the bank is experiencing a decreasing trend in slippages.
Growth Aspects
- The Bank is confident about future growth, particularly due to rate cuts. While the repricing of the bank’s advances may not happen immediately, deposit refinancing could occur sooner.
- The bank has taken substantial steps to reinforce its business, deploying over 100 agricultural field officers, both newly recruited and internally reassigned. Additionally, it has developed its direct sales agent (DSA) and direct sales team (DST) networks around the country for business sourcing.
- A primary focus area is the bank’s credit reform program, aiming at streamlining operations, reducing turnaround time, and adopting policy adjustments. Consequently, the bank is building up Retail Assets Centers at several locations where DST-sourced applications may be lodged, vetted, and inspected efficiently.
- For MSMEs and mid-corporate clients, It wants to deploy dedicated relationship and coverage teams across multiple regions to boost customer engagement and service.
- On the branch side, the bank has boosted its liability acquisition operations by boosting sales leads. It is also deploying 300+ CASA officers and “feet on street” staff for sourcing. With positive results, the bank aims to double this crew in the future.
- The bank is also preparing to launch a range of new solutions, including a trading platform coupled with its existing third-party products like insurance. Additionally, Karnataka Bank will establish a wealth management platform in partnership with others to provide comprehensive financial services to its consumers.
(K) Strengths & Weaknesses of Karnataka Bank
Strengths
(i) Improvement in capital adequacy levels boosted by equity infusion and continuous profitability
Aided by consistent profit accretion and the completion of a ₹1,500 crore equity raise through preferential allotment and qualified institutional placement(QIP) in three tranches during FY24, Karnataka Bank’s total capital adequacy ratio (CAR) and Tier-I CAR improved to 18.00% and 15.93%, respectively, as of March 31, 2024, compared to 17.45% and 14.18% as of March 31, 2023. As of Sept 2024, the bank’s CAR and Tier-I CAR stood at 17.58% and 15.93%, respectively, excluding earnings for the quarter, remaining comfortably over the regulatory requirements.
(ii) Improved CASA deposits led to a more stable and granular resource profile
The bank’s deposit base has remained stable and sticky, comprising 85.2% of total liabilities. As of March 31, 2024, the bank’s deposit profile was robust, with 88.68% of deposits under ₹2 crore. External borrowings are confined to Tier II bonds, RBI, and other financial institutions. As of March 31, 2024, the percentage of low-cost CASA deposits remained largely unchanged at 31.97%. However, the rate has moderated to 30.82% as of Sept 2024. The Bank’s ability to increase CASA deposit share is vital for raising deposits at competitive rates.
Weaknesses
(i) Moderate asset quality, but a sharp reduction in stressed assets during FY24 and Q2 FY25
Karnataka Bank’s GNPA improved to 3.53% (from 3.74%) and NNPA to 1.58% (from 1.70%) due to write-offs and fewer new bad loans in FY24. In 2024, GNPA was stable at 3.21%. The slippage ratio dropped to 2.80% in FY24 (from 3.31%). Provision coverage, including written-off accounts, was 80.14% (up from 77%).
(ii) Continues to be regionally concentrated
KBL is a medium-sized bank in India, with a total business of over ₹1.5 lakh crore in FY24 and projected to reach ₹1.76 lakh crore. However, the bank’s operations remain regionally concentrated, with Karnataka accounting for roughly 45.77% of total credit exposure as of June 30, 2024, a minor decrease from 45.8% the previous year. Furthermore, as of March 31, 2024, the top five states jointly account for 85.93% of the bank’s overall credit exposure, compared to 83.16% last year.
Drop us your query at – info@pawealth.in or Visit pawealth.in
References: Annual Reports, News Publications, Investor Presentations, Corporate Announcements, Management Discussions, Analyst Meets and Management Interviews, Industry Publications.
Disclaimer: The report only represents the personal opinions and views of the author. No part of the report should be considered a recommendation for buying/selling any stock. Thus, the report & references mentioned are only for the information of the readers about the industry stated.
Most successful stock advisors in India | Ludhiana Stock Market Tips | Stock Market Experts in Ludhiana | Top stock advisors in India | Best Stock Advisors in Gurugram | Investment Consultants in Ludhiana | Top Stock Brokers in Gurugram | Best stock advisors in India | Ludhiana Stock Advisors SEBI | Stock Consultants in Ludhiana | AMFI registered distributor | Amfi registered mutual fund | Be a mutual fund distributor | Top stock advisors in India | Top stock advisory services in India | Best Stock Advisors in Bangalore
The post Karnataka Bank Ltd. – From Regional Giant to National Player appeared first on PA Wealth.