The massive demographic shift we see today, with the world’s population continuing to grow and age as life expectancy continues to rise, is due in part to the advances in medicine in the last 50 years. But at the same time, these achievements put additional strain on healthcare systems built in the 1950s, which need to provide services to the growing number of patients and simultaneously adapt to cope with new threats.
While the need for modernization of healthcare is obvious, the Covid-19 pandemic has become a major booster. In 2021 Accenture’s Digital Health Technology Vision report 81% of healthcare executives stated that the pace of digital transformation was accelerating in their company. This transformation not only eliminates paper forms but also revolutionizes the way patients and clinicians interact. By leveraging patient data, it enables more personalized treatment and earlier disease detection, fundamentally changing the approach to healthcare. The Covid-19 pandemic has also accelerated the demand for secure remote health strategies and integrated systems for communication, automation, and medical technologies.
Patient data is gathered with the help of a range of connected devices that oftentimes are referred to as a subdivision of IoT – the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). IoMT devices fall into many categories: from large equipment such as robotic arms or MRI scanners to smaller units such as infusion pumps, glucose meters, smart thermometers and heart rate monitors, and even tiny ingestible sensors and cameras that perform endoscopies. Traditionally, these connected devices relied on ethernet cables, Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, which either required infrastructure upgrade (experts say that hospitals are running out of room for cables) or had certain limitations on the number of connected devices.
Cellular connectivity proved to be not only the solution for these problems, but also a major enabler of new use cases: for instance, it helps to connect devices in rural areas that were left out of such healthcare programs earlier. Another advantage of cellular technology is that it enables IoMT devices to work right out of the box. It is important both for patients that can implement them at home and for providers that don’t need additional staff to set them up.
Cellular network technology, particularly 5G, has been critical in running medical services during and after the pandemic. With download and upload speeds faster than 4G, 5G-backed medical technologies have supported significant advancements, such as real-time telemedicine, remote surgeries, and AI-assisted diagnostics. 6G could promise even more transformative potential. According to a recent Kaleido Intelligence forecast, by 2028, the number of cellular connections in healthcare is going to increase almost three times and annual data consumption will grow 400% to over 140 million petabytes.
With hundreds of types of connected devices in healthcare, let’s look at four main use case categories where cellular technology plays a critical role.

Telemedicine
Before the pandemic, telemedicine usage was limited. In 2019, roughly 0.3% of all healthcare interactions in the US occurred online. During the first three months of the pandemic, usage surged more than 750%, as telemedicine accounted for nearly 24% of all interactions. Now it’s an integral part of the healthcare landscape, and patients consider it as good or better than a standard in-person visit. However, oftentimes the telehealth programs coverage is inadequate. For instance, more than 100 million Americans today live in healthcare deserts, lack access to primary care providers and hospitals, and also the digital infrastructure needed for remote care.
Cellular connectivity can be critical in this case, particularly for telehealth programs in rural areas or even for patients at sea, onboard ships. Another application is connecting devices that first responders are using out in the field. It allows to take advantage of consultation with subject-matter experts over video, which is very important for early diagnostics, to do either treatment in place, or to make sure the patient gets delivered to the right hospital.
Remote Patient Monitoring
This type of use cases is mostly relevant for chronic conditions or acute recovery at home. The category includes IoMT devices like smart wearables or blood pressure monitors, scales tracking weight, blood glucose meters, portable ECGs or smart fusion pumps. These devices offer a significant improvement in quality of life for people with chronic conditions, who would otherwise be restricted to stationary devices within the walls of a hospital. Moreover, in many cases they are beneficial not only for patients, but also to healthcare organizations, since they relieve time and resource pressures and help with equipment availability, workflow management and dealing with patient intake.
As IoMT includes not only small devices, cellular connectivity is instrumental in getting data both from wearables or “nearables” and medical equipment that goes out for portable imaging systems, or supports care at home. The ability to move this equipment from hospitals and still have it connected is key for remote monitoring scenarios of all types.
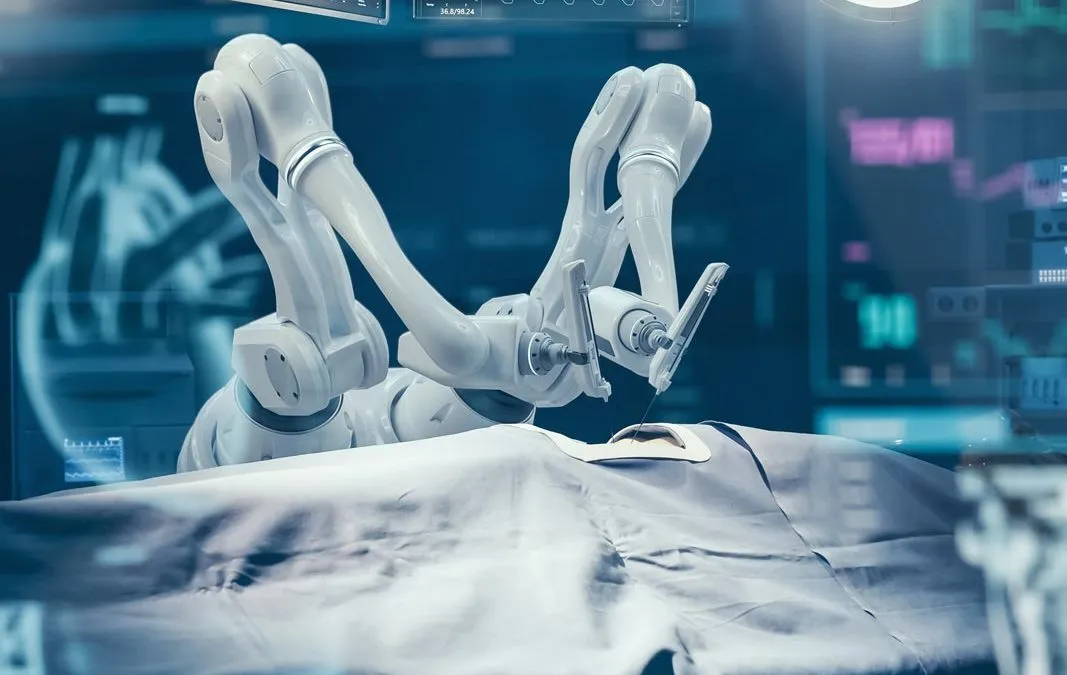
Robotic Surgeries
Robotic surgical systems have been developed and used for over 40 years. Highly complex surgical robots can either aid a human surgeon or even execute operations by themselves: certain orthopedic procedures including knee and hip replacements are sometimes carried out robotically. In a remote surgery scenario, the entire treatment procedure is executed by a surgeon at a remote site, while his hands are replaced by robotic arms. It can be applicable in ambulances, disaster situations or remote areas requiring precise control and feedback communication mechanisms for surgeons.
Cellular connectivity plays a key role in these scenarios because of its low latency. Just recently, a doctor performed a landmark remote robotic surgery from Rome on a patient in Beijing, 5,000 miles away. The surgery was performed through a set of robotic arms with the help of a 5G network.
Medical Deliveries
Cellular connectivity can be used to monitor medical transport containers for temperature, location, and tampering. Vaccine shipments, for example, need such monitoring to maintain a required, constant low temperature, while medical equipment or other valuable medical supplies must be monitored for tampering.
Besides, along with robots, there are drones: although they aren’t IoMT devices per se, they are widely used for medical deliveries. In many cases, it’s the way to optimize existing procedures and make them faster and more efficient, like having medicines flown to seafarers who fall sick or delivering defibrillators faster than the ambulance. They are also used to transport vaccines, medication, blood and other samples, and diagnostic kits.

Connectivity Requirements
In healthcare, most of the connectivity usage scenarios are mission-critical, and therefore have very strict requirements. They differ depending on the use case, but each of the healthcare scenarios can be very demanding in terms of connectivity in one or even several criteria. Besides, it’s important to remember that healthcare is a heavily regulated environment, where certain use cases need clearance from FDA or other regulators, and therefore some connectivity characteristics may also be critical in this regard.
Coverage
Coverage is critical for all use cases in healthcare, no matter if devices need to be connected in the hospital, in a rural area or in an ambulance. Cellular networks are a great connectivity option in that regard because of their ubiquitousness. In certain use cases that require stable coverage for a large number of devices that need to be connected simultaneously, hospitals may set up private networks.
Latency
Remote patient monitoring and robotic surgeries require an ultra-reliable connection with very low latency. For example, the feedback to the surgeon must be as immediate as possible to ensure that his actions are not slowed or limited by network latency, and haptic feedback to the surgeon where they “feel” the resistance of their tool as it cuts has a round-trip time requirement of as low as 1 ms. Technically, cellular networks, 5G networks in particular, are capable of providing low latency for this and many other use cases in healthcare. The actual latency would depend on the architecture of the operator’s core network, so in certain scenarios it will be an important factor.
Reliability
Cellular connectivity is also essential for reasons of reliability, particularly when it comes to operating robotic arms or drones beyond visual line of sight. In a test with two cellular operators and a simple dual network redundancy enhancement which implied packet duplication, LTE networks supported 99.9 percent reliability. With 5G standard techniques, this packet duplication can be achieved even over a single network.
Security
The nature of the data that is transmitted by IoMT devices implies the highest level of security. Cellular networks, in general, have been built with security in mind. Moreover, one of the primary considerations in 5G development was to make sure that security was an integral part of its architecture and design.

Webbing’s Solution
Webbing offers a connectivity solution that ensures global access to reliable and high-quality internet, with low latency and the best of class coverage. It provides secure and continuous internet connection for IoMT devices, wherever they need it.
As a global MVNO, Webbing’s network of 600+ mobile operators guarantees world-wide coverage. It allows to roam on several carriers’ networks in every region, solving the problem of weak spots that any mobile network may have and ensuring full coverage and continuous connectivity even at remote locations.
Webbing is a global connectivity provider with a distributed full core network with local breakouts, multiple network solution, and data server redundancy that provides connectivity stability and low latency. As such, Webbing’s network is well suited to support mission-critical, high-data consumption type of use cases. It also allows for compliance with all types of connectivity regulations.
Our eSIM solution ensures failover connectivity with the capability of using multiple mobile carrier profiles, easily changing carriers at any time with zero integration, and an option to fall back from a failing profile to a different profile without any need to communicate with a remote server or deal with multiple SIM cards.
A flexible approach to data packages allows us to tailor our connectivity offering for every customer based on the type of connected devices and their data consumption needs as well as the locations where the devices are used, aiming at overall optimization of the total cost of operations for the client.
Our solutions help enterprises overcome their connectivity challenges and optimize costs for global deployments, providing the benefits of roaming with multiple carrier options in every country, and seamless transition between carriers, while maintaining low rates and low latency on a global scale with a single SIM.
Reach out to learn more.
The post How Cellular Connectivity is Revolutionizing Healthcare appeared first on Webbing.




